Partnership on intricate advancement tasks often provides difficulties. For conventional software application tasks, these difficulties are popular, and throughout the years a variety of methods to resolving them have actually developed. However as artificial intelligence (ML) ends up being a vital element of increasingly more systems, it positions a brand-new set of difficulties to advancement groups. Chief amongst these difficulties is getting information researchers (who use a speculative method to system design advancement) and software application designers (who depend on the discipline enforced by software application engineering concepts) to work harmoniously.
In this SEI article, which is adjusted from a just recently released paper to which I contributed, I highlight the findings of a research study on which I coordinated with associates Nadia Nahar (who led this work as part of her PhD research studies at Carnegie Mellon University and Christian Kästner (likewise from Carnegie Mellon University) and Shurui Zhou (of the University of Toronto). The research study looked for to recognize partnership difficulties typical to the advancement of ML-enabled systems. Through interviews performed with many people taken part in the advancement of ML-enabled systems, we looked for to address our main research study concern: What are the partnership points and matching difficulties in between information researchers and engineers? We likewise analyzed the impact of different advancement environments on these tasks. Based upon this analysis, we established initial suggestions for resolving the partnership difficulties reported by our interviewees. Our findings and suggestions notified the abovementioned paper, Partnership Difficulties in Structure ML-Enabled Systems: Interaction, Documents, Engineering, and Process, which I’m happy to state gotten a Distinguished Paper Award at the 44th International Conference on Software Application Engineering (ICSE 2022).
In spite of the attention ML-enabled systems have actually drawn in– and the guarantee of these systems to go beyond human-level cognition and stimulate terrific advances– moving a machine-learned design to a practical production system has actually shown extremely hard. The intro of ML needs higher competence and presents more partnership points when compared to conventional software application advancement tasks. While the engineering elements of ML have actually gotten much attention, the nearby human elements worrying the requirement for interdisciplinary partnership have not.
The Existing State of the Practice and Its Limitations
Many software application tasks extend beyond the scope of a single designer, so partnership is a must. Developers generally divide the work into different software application system parts, and employee work mostly individually till all the system parts are prepared for combination. As a result, the technical crossways of the software application parts themselves (that is, the element user interfaces) mostly identify the interaction and partnership points amongst advancement employee.
Difficulties to partnership take place, nevertheless, when employee can not quickly and informally interact or when the work needs interdisciplinary partnership. Distinctions in experience, expert backgrounds, and expectations about the system can likewise posture difficulties to reliable partnership in conventional top-down, modular advancement tasks. To help with partnership, interaction, and settlement around element user interfaces, designers have actually embraced a series of methods and typically use casual broadcast tools to keep everybody on the exact same page. Software application lifecycle designs, such as waterfall, spiral, and Agile, likewise assist designers strategy and style steady user interfaces.
ML-enabled systems typically include a structure of conventional advancement into which ML element advancement is presented. Establishing and incorporating these parts into the bigger system needs separating and collaborating information science and software application engineering work to establish the found out designs, work out the element user interfaces, and prepare for the system’s operation and development. The found out design might be a small or significant element of the general system, and the system generally consists of parts for training and keeping an eye on the design.
All of these actions indicate that, compared to conventional systems, ML-enabled system advancement needs competence in information science for design structure and information management jobs. Software application engineers not trained in information science who, nonetheless, handle design structure tend to produce inefficient designs On the other hand, information researchers tend to choose to concentrate on modeling jobs to the exemption of engineering work that may affect their designs. The software application engineering neighborhood has actually just just recently started to take a look at software application engineering for ML-enabled systems, and much of this work has actually focused directly on matters such as screening designs and ML algorithms, design release, and design fairness and toughness. Software application engineering research study on embracing a system-wide scope for ML-enabled systems has actually been restricted.
Framing a Research Study Method Around Real-World Experience in ML-Enabled System Advancement
Finding restricted existing research study on partnership in ML-enabled system advancement, we embraced a qualitative technique for our research study based upon 4 actions: (1) developing scope and performing a literature evaluation, (2) talking to specialists developing ML-enabled systems, (3) triangulating interview findings with our literature evaluation, and (4) verifying findings with interviewees. Each of these actions is talked about listed below:
- Scoping and literature evaluation: We analyzed the existing literature on software application engineering for ML-enabled systems. In so doing, we coded areas of documents that either straight or implicitly attended to partnership problems amongst employee with various abilities or instructional backgrounds. We examined the codes and obtained the partnership locations that notified our interview assistance.
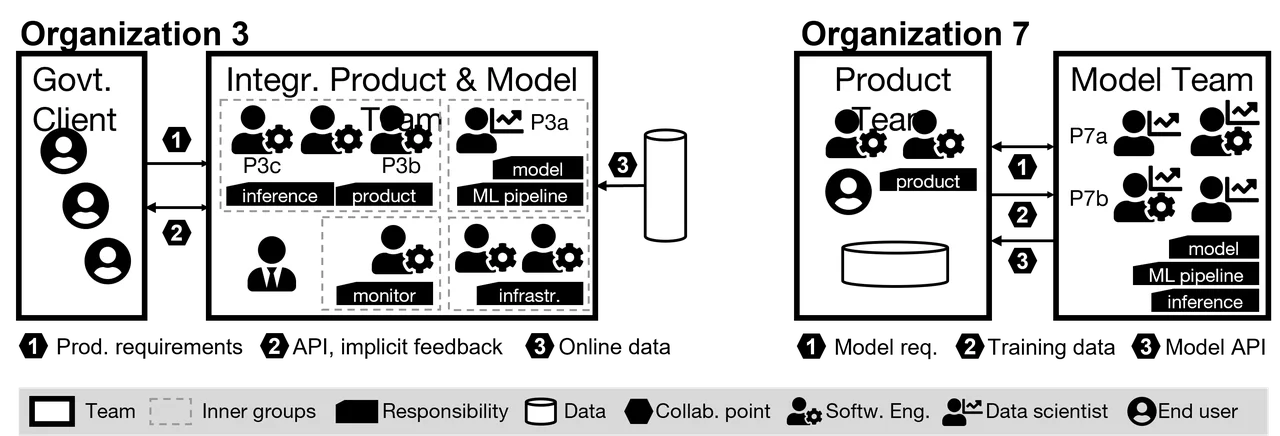
- Interviews: We performed interviews with 45 designers of ML-enabled systems from 28 various companies that have actually just just recently embraced ML (see Table 1 for individual demographics). We transcribed the interviews, and after that we developed visualizations of organizational structure and duties to map difficulties to partnership points (see Figure 1 for sample visualizations). We even more examined the visualizations to identify whether we might associate partnership issues with particular organizational structures.
- Triangulation with literature: We linked interview information with associated conversations determined in our literature evaluation, in addition to possible options. Out of the 300 documents we check out, we determined 61 as potentially appropriate and coded them utilizing our codebook.
- Credibility check: After developing a complete draft of our research study, we offered it to our interviewees in addition to supplemental product and concerns triggering them to look for accuracy, locations of arrangement and dispute, and any insights acquired from checking out the research study.
. Table 1: Individual and Business Demographics
.
.
.
|
.
.
Type
. . |
.
. . |
|
.
. . |
.
. . |
|
. 5 years of experience or more( 28 ) , 2-5 years (9 ), less . than 2 years (8 ) . (* ) . (* ) .
. . |
.
.(* ) . . Huge tech( 6), Non-IT (4), Mid-size tech( 11), Start-up( 5), . Consulting( 2) . |
|
.
.(* )Business Area( 28) . . . . |
. The United States And Canada( 11 ), South America (1), Europe( 5), Asia
. (10), Africa (1)
.(* )
.
. . |
| requirements and preparation
training information product-model combination Browsing the Tensions In Between Item and Design Requirements To start, we discovered essential distinctions in the order in which groups recognize item and design requirements: Design initially |
Item initially
(13 of 28 companies): These groups begin with item advancement and after that establish a design to support it. Frequently, the item currently exists, and brand-new ML advancement looks for to improve the item’s abilities. Design requirements are originated from item requirements, which typically constrain design qualities. Parallel |
It’s difficult to generate item requirements without a strong understanding of ML abilities, so the design group need to be associated with the procedure early. Information researchers reported needing to compete with impractical expectations about design abilities, and they regularly needed to inform customers and designers about ML strategies to remedy these expectations. Where a product-first advancement trajectory is practiced, it was possible for the item group to disregard information requirements when working out item requirements. Nevertheless, when requirements event is delegated the design group, essential item requirements, such as functionality, may be disregarded.
Design advancement with uncertain requirements prevails
In spite of an expectation they will work individually, design groups hardly ever get sufficient requirements. Typically, they take part in their work without a total understanding of the item their design is to support. This omission can be a tough issue for groups that practice model-first advancement.
- Offered design requirements hardly ever surpass precision and information security
- Neglecting other essential requirements, such as latency or scalability, has actually triggered combination and operation issues.
- Fairness
and
explainability
- requirements are hardly ever thought about. Suggestions
- Requirements and preparation form a crucial partnership point for item and design groups establishing ML-enabled systems. Based upon our interviews and literature evaluation, we have actually proposed the list below suggestions for this partnership point: Include information researchers early while doing so.
- Think about embracing a parallel advancement trajectory for item and design groups. Conduct ML training sessions to inform customers and item groups.
Embrace more official requirements paperwork for both design and item.
- Attending To Difficulties Connected To Training Data Our research study exposed that arguments over training information represented the most typical partnership difficulties. These arguments typically come from the truth that the design group regularly does not own, gather, or comprehend the information. We observed 3 organizational structures that affect the partnership difficulties associated with training information:
- Offered information: The item group supplies information to the design group. Coordination tends to be far-off and official, and the item group holds more power in settlements over information.
- External information: The design group depends on an external entity for the information. The information typically originates from openly readily available sources or from a third-party supplier. When it comes to openly readily available information, the design group has little working out power. It holds more working out power when employing a 3rd party to source the information. Internal information: Item, design, and information groups all exist within the exact same company and utilize that company’s internal information. In such cases, both item and design groups require to conquer settlement difficulties associated with information utilize coming from varying top priorities, consents, and information security requirements. Lots of interviewees kept in mind discontentment with information amount and quality. One typical issue is that the item group typically does not have understanding about quality and quantity of information required. Other information issues typical to the companies we analyzed consisted of the following: Offered and public information are typically insufficient
Research Study
- has actually raised concerns about the representativeness and reliability of such information. Training alter prevails: designs that reveal appealing outcomes throughout advancement stop working in production environments due to the fact that real-world information varies from the offered training information.
- Information comprehending and access to information professionals typically present traffic jams
- Information paperwork is practically never ever sufficient. Employee typically gather info and keep an eye on the information in their heads. Design groups who get information from item groups have a hard time getting aid from the item group to comprehend the information. The exact same holds for information acquired from openly readily available sources. Even internal information typically struggles with developing and inadequately recorded information sources.
- Uncertainty develops when employing an information company
Trouble often develops when a design group looks for buy-in from the item group on employing an external information company. Individuals in our research study kept in mind interaction ambiguity and covert presumptions as essential difficulties while doing so. Expectations are interacted verbally, without clear paperwork. As a result, the information group typically does not have enough context to comprehend what information is required.
There is a requirement to manage developing information
- Designs require to be frequently re-trained with more information or adjusted to modifications in the environment. Nevertheless, in cases where information is offered constantly, design groups have a hard time to guarantee consistency gradually, and many companies do not have the facilities to keep an eye on information quality and amount. Internal top priorities and security issues typically block information gain access to
- Typically, internal tasks are regional efforts with a minimum of some management buy-in however little buy-in from other groups concentrated on their own top priorities. These other groups may question business worth of the task, which may not impact their location straight. When information is owned by a various group within the company, security issues over information sharing typically emerge. Training information of enough quality and amount is essential for establishing ML-enabled systems. Based upon our interviews and literature evaluation, we have actually proposed the list below suggestions for this partnership point:
- When preparation, budget plan for information collection and access to domain professionals (or perhaps a devoted information group). Embrace an official agreement that defines information quality and amount expectations.
When dealing with a devoted information group, make expectations extremely clear.
- Think about utilizing an information recognition and tracking facilities early in the task. Difficulties Incorporating the Item and Design in ML-Enabled Systems At this partnership point, information researchers and software application engineers require to work carefully together, regularly throughout numerous groups. Disputes typically take place at this point, nevertheless, coming from uncertain procedures and duties. Differing practices and expectations likewise produce stress, as does the method which engineering duties are appointed for design advancement and operation. The difficulties dealt with at this partnership point tended to fall under 2 broad classifications: culture clashes amongst groups with varying duties and quality control for design and task. Interdisciplinary Partnership and Cultural Clashes
- We observed the following disputes coming from distinctions in software application engineering and information science cultures, all of which were enhanced by an absence of clearness about duties and limits: Group duties typically do not match abilities and choices
- Information researchers revealed discontentment when pushed to handle engineering jobs, while software application engineers typically had inadequate understanding of designs to successfully incorporate them. Siloing information researchers promotes combination issues
- Information researchers typically operate in seclusion with weak requirements and an absence of understanding of the bigger context. Technical lingo difficulties interaction
- The varying terms utilized in each field results in uncertainty, misconception, and malfunctioning presumptions. Code quality, paperwork, and versioning expectations vary commonly
Software application engineers asserted that information researchers do not follow the exact same advancement practices or comply with the exact same quality requirements when composing code.
- Lots of disputes we observed associate with limits of obligation and varying expectations. To resolve these difficulties, we proposed the list below suggestions:
- Specify procedures, duties, and limits more thoroughly.
- File APIs at partnership points.
- Employee committed engineering assistance for design release.
Do not silo information researchers.
Establish typical terms.
Interdisciplinary Partnership and Quality Control for Design and Item
Throughout advancement and combination, concerns of obligation for quality control typically emerge. We kept in mind the following difficulties:
- Objectives for design adequacy are difficult to develop The design group often assesses the precision of the design, however it has problem choosing whether the design suffices owing to an absence of requirements.
- Self-confidence is restricted without transparent design examination Design groups do not focus on examination, so they typically have no organized examination technique, which in turn results in uncertainty about the design from other groups.
- Duty for system screening is uncertain Groups typically deal with evaluating the whole system after design combination, with design groups regularly presuming no obligation for item quality.
- Preparation for online screening and tracking is unusual Though essential to keep an eye on for training alter and information drift, such screening needs the coordination of groups accountable for item, design, and operation. Additionally, numerous companies do not do online screening due to the absence of a basic procedure, automation, or perhaps test awareness.
Based upon our interviews and the insights they offered, we established the list below suggestions to resolve difficulties associated with quality control:
- Focus on and prepare for quality control screening.
- The item group ought to presume obligation for general quality and system screening, however it needs to engage the design group in the production of a tracking and experimentation facilities.
- Prepare for, budget plan, and appoint structured feedback from the item engineering group to the design group.
- Evangelize the advantages of screening in production.
- Specify clear quality requirements for design and item.
Conclusion: 4 Locations for Improving Partnership on ML-Enabled System Advancement
Information researchers and software application engineers are not the very first to recognize that interdisciplinary partnership is tough, however assisting in such partnership has actually not been the focus of companies establishing ML-enabled systems. Our observations show that difficulties to partnership on such systems fall along 3 partnership points: requirements and task preparation, training information, and product-model combination. This post has actually highlighted our particular findings in these locations, however we see 4 broad locations for enhancing partnership in the advancement of ML-enabled systems:
- Interaction: To fight issues developing from miscommunication, we promote ML literacy for software application engineers and supervisors, and also software application engineering literacy for information researchers.
- Documents: Practices for recording design requirements, information expectations, and guaranteed design qualities have yet to settle. User interface paperwork currently in usage might offer an excellent beginning point, however any method needs to utilize a language comprehended by everybody associated with the advancement effort.
- Engineering: Task supervisors ought to guarantee enough engineering abilities for both ML and non-ML parts and foster item and operations believing.
- Process: The speculative, trial-and mistake procedure of ML design advancement does not naturally line up with the conventional, more structured software application procedure lifecycle. We promote for additional research study on incorporated procedure lifecycles for ML-enabled systems.